
- #CF CARD RECOVERY MALFUNCTION ARCHIVE#
- #CF CARD RECOVERY MALFUNCTION WINDOWS#
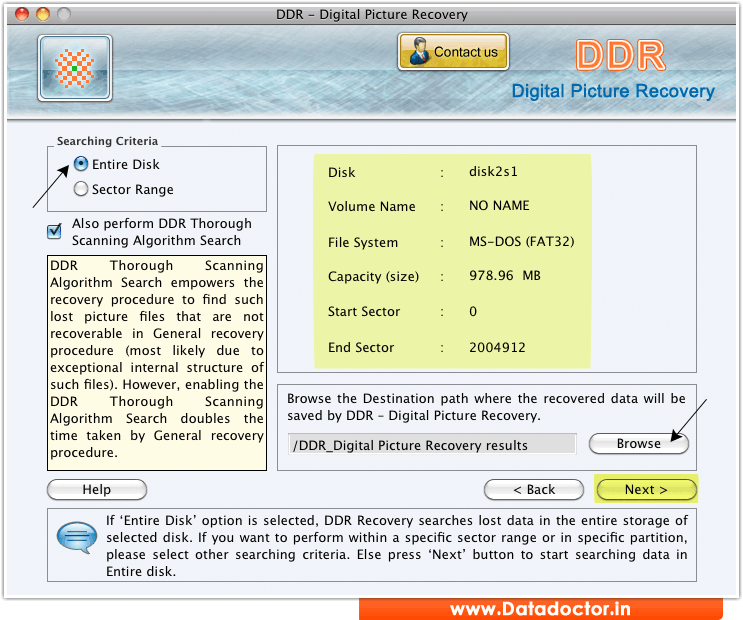
TestDisk displays the partition table types. If available, use raw device /dev/rdisk* instead of /dev/disk* for faster data transfer. Use up/down arrow keys to select your hard drive with the lost partition/s.Choose None if you do not want messages and details of the process to be written into a log file (useful if for example Testdisk was started from a read-only location).Īll hard drives should be detected and listed with the correct size by TestDisk:.Choose Create to instruct Testdisk to create a log file containing technical information and messages, unless you have a reason to append data to the log or you execute TestDisk from read only media and must create the log elsewhere.testdisk /dev/md0 to repair a filesystem on top of a Linux RAID device.The same method works with filesystem encrypted with cryptsetup/dm-crypt/LUKS.
 testdisk /dev/mapper/truecrypt0 or testdisk /dev/loop0 to repair the NTFS or FAT32 boot sector files from a TrueCrypt partition. To repair a filesystem not listed by TestDisk, run testdisk device, i.e. testdisk 'image.?' if the Encase image is split into several files. testdisk image.E01 to recover files from an Encase EWF image. testdisk image.dd to work from a raw disk image. To recover partition from a media image or repair a filesystem image, run Under OS/2, TestDisk doesn't handle a physical device, only a disk image. Under MacOSX, if you are not root, TestDisk (ie testdisk-6.13/testdisk) will restart itself using sudo after confirmation on your part. Under Unix/Linux/BSD, you need to be root to run TestDisk (ie. Under Vista, right-click testdisk_win.exe and then "Run as administrator" to launch TestDisk. Under Windows, start TestDisk (ie testdisk-6.13/testdisk_win.exe) from an account in the Administrator group. To recover a lost partition or repair the filesystem from a hard disk, USB key, Smart Card, etc., you need enough rights to access a physical device.
testdisk /dev/mapper/truecrypt0 or testdisk /dev/loop0 to repair the NTFS or FAT32 boot sector files from a TrueCrypt partition. To repair a filesystem not listed by TestDisk, run testdisk device, i.e. testdisk 'image.?' if the Encase image is split into several files. testdisk image.E01 to recover files from an Encase EWF image. testdisk image.dd to work from a raw disk image. To recover partition from a media image or repair a filesystem image, run Under OS/2, TestDisk doesn't handle a physical device, only a disk image. Under MacOSX, if you are not root, TestDisk (ie testdisk-6.13/testdisk) will restart itself using sudo after confirmation on your part. Under Unix/Linux/BSD, you need to be root to run TestDisk (ie. Under Vista, right-click testdisk_win.exe and then "Run as administrator" to launch TestDisk. Under Windows, start TestDisk (ie testdisk-6.13/testdisk_win.exe) from an account in the Administrator group. To recover a lost partition or repair the filesystem from a hard disk, USB key, Smart Card, etc., you need enough rights to access a physical device. #CF CARD RECOVERY MALFUNCTION ARCHIVE#
Extract the files from the archive including the sub-directories. If TestDisk is not yet installed, it can be downloaded from TestDisk Download.
#CF CARD RECOVERY MALFUNCTION WINDOWS#
The Windows Disk Management Console now displays only "unallocated space" where this logical partition had been located. In Windows Explorer, that logical drive is no longer available.
Windows Explorer or Disk Manager displays the first primary partition as raw (unformatted) and Windows prompts: The drive is not formatted, do you want to format it now?. If the hard disk was a secondary (data) drive or you can connect the drive to another computer in its secondary channel (usually where a CD/DVD drive is connected), the following symptoms would be observed: If this hard disk's primary partition contained an operating system, it would most likely no longer boot up - due to its corrupted boot sector. To actually write partition data to the MBR, you must choose the "Write" selection and press the Enter key. To save modifications under TestDisk, you must confirm them with the y (Yes) and/or Enter keys, and. To return to a previous display or quit TestDisk, use the q (Quit) key. To proceed, confirm your choice(s) with the Enter key. To navigate in TestDisk, use the Arrow and PageUp/PageDown keys. TestDisk must be executed with Administrator privileges. For Information about FAT12, FAT16, ext2/ext3, HFS+, ReiserFS and other partition types, read Running the TestDisk Program. Other recovery examples are also available. Recovery of a FAT32 partition (instead of an NTFS partition) can be accomplished by following exactly the same steps. recovering the accidentally deleted logical NTFS partition. rewriting the corrupted NTFS boot sector, and. This recovery example guides you through TestDisk, step by step, to recover these 'lost' partitions by: a logical NTFS partition has been accidentally deleted. the boot sector of the primary NTFS partition has been damaged, and. We have a 36GB hard disk containing 3 partitions. 10 A partition is still missing: Deeper Search. 
9 Save the partition table or search for more partitions?.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
